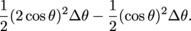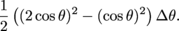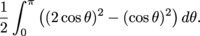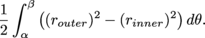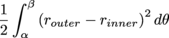We're gunning for the area of this region here: 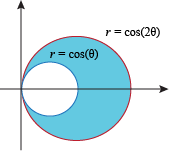
Let's find the area inside the graph r = 2cos θ and subtract the area inside the graph r = cos θ. The area inside r = 2cos θ is 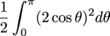
and the area inside r = cos θ is 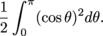
So the area of the region in between the two graphs is 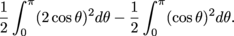
Since the limits of integration on the two integrals are the same, we can combine them into the single integral 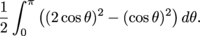
We could also find this area one slice at a time. That is, we could find the area of the region between the graphs r = 2cos θ and r = cos θ by slicing the larger region into pizza slices, figuring out the area of the "crust" on each slice, and adding those areas up. The area of the full slice is 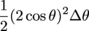
and the area of the juicy center part is  , ,
so the area of the crust is 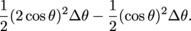
This simplifies to 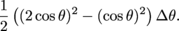
When we add up all all the crust areas and let the number of pieces approach ∞, we get the integral 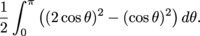
To generalize with a nice, neat, pizza-making formula, when we have a graph router and a graph rinner, the area in between the graphs for α ≤ θ ≤ β is 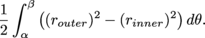
Be Careful: When working with two different radii, we don't want the formula below, 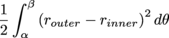
for the area between the graphs router and rinner. This may look less complicated, but it's wrong. The two radii must be squared separately and then subtracted. | 
 to
to  .
. .
.




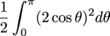
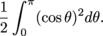
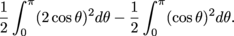
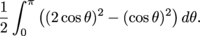
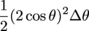
 ,
,