ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Playlist AP® Physics 2: Object Interaction and Forces 7 videos
AP Physics 2: 1.2 Object Interaction and Forces. What is the acceleration experienced by the feather?
AP Physics 2: 1.3 Object Interaction and Forces. What is the magnitude of the current L in the wire?
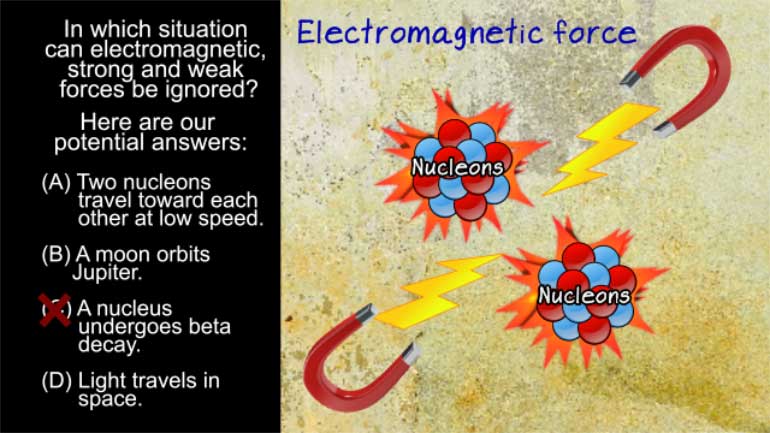
AP Physics 2: 2.1 Object Interaction and Forces. Which of the following is not one of the four fundamental forces?
AP Physics 2: 2.3 Object Interaction and Forces 171 Views
Share It!
Description:
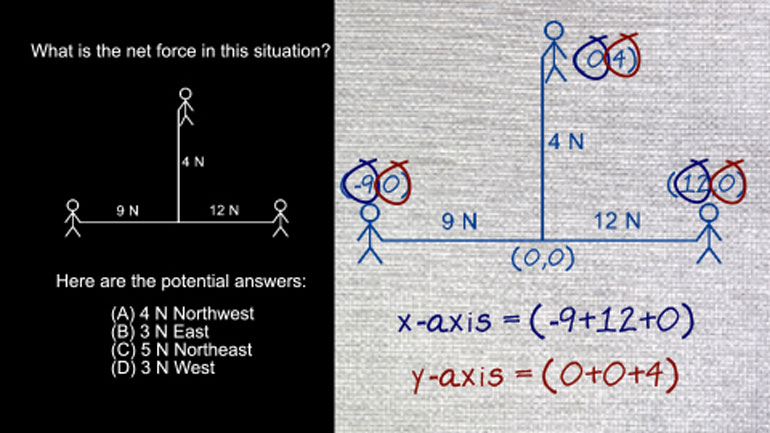
AP Physics 2: 2.3 Object Interaction and Forces. What is the net force in this situation?
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak Then here's your smoke too Sure
- 00:06
Brought to you by tug of war which combines all
- 00:08
the fun of being dragged into the mud with the
- 00:11
pain of rope burns Yeah Why do people do this
- 00:14
All right Well three friends engage in a competition of
Full Transcript
- 00:17
tug of war over They didn't pay attention in physics
- 00:20
Instead of dispersing themselves equally they distributed themselves as in
- 00:25
the diagram scene right chair with one person on either
- 00:28
side And one person in between The person on the
- 00:31
left pulls with a force of nine Newton's The person
- 00:34
on the right pulls with a force of twelve noons
- 00:36
and the person this guy right here on top pulls
- 00:38
with a force of four news what's the net force
- 00:42
in this situation and here the potential answer sounds like
- 00:47
a movie star Cary grant Okay well this will be
- 00:50
quite the interesting tug a war match Let's Just hope
- 00:53
no one gets hurt Is there drag along the ground
- 00:55
but looking at the set up here we know we're
- 00:57
dealing with vectors And to find the total sum of
- 01:00
vector forces we can add them up Yeah once your
- 01:04
vector Victor All right Well let's think of this three
- 01:07
headed monster as if it was on a coordinate plane
- 01:10
A different kind of plain The middle point will be
- 01:13
zero for both axes The first time pulling toward the
- 01:16
left will be a point negative nine zero And the
- 01:19
person pulling toward the right will be a point Twelve
- 01:22
zero The guy pulling up one The one who doesn't
- 01:25
understand how war works and is really messing up the
- 01:28
whole shebang Yeah well he'll have y coordinate of zero
- 01:31
comma four right there Now we can add the x
- 01:33
and y components Tto find the net force Well the
- 01:36
net force along the x axis equals negative nine plus
- 01:39
twelve plus zero And along the y axis it equals
- 01:43
zero plus zero plus four So that gives us a
- 01:46
net force along the x axis of three And along
- 01:48
the y axis of four Now because these forces are
- 01:52
in a right angle to each other we can use
- 01:54
the pythagorean theorem toe Add them together Little pythagoras taught
- 01:58
the world that a squared plus b squared equals c
- 02:02
squared that we can plug in our numbers and find
- 02:05
that the net force Vector is five and while we
- 02:08
don't have the exact direction we know that the forces
- 02:11
are being applied to the north and to the east
- 02:15
Well in our coordinate playing the force will be in
- 02:17
the upper right quadrant All of this tells us that
- 02:20
the answer is c right there five in northeast when
- 02:24
we're dealing with vector edition diagrams are always helpful so
- 02:28
draw a little sketch on the test to make it
- 02:30
clear There's No reason to struggle harder than you need
- 02:32
that's True in physics or in tug of war sometimes
- 02:35
the best way to win Yeah just let go No
Related Videos
AP Physics 2: 1.1 Properties of Objects and Systems. What is the magnitude and direction of the conventional current in this wire?
AP Physics 2: 1.5 Properties of Objects and Systems. According to the Bohr's model of the atom, which of the following are true?
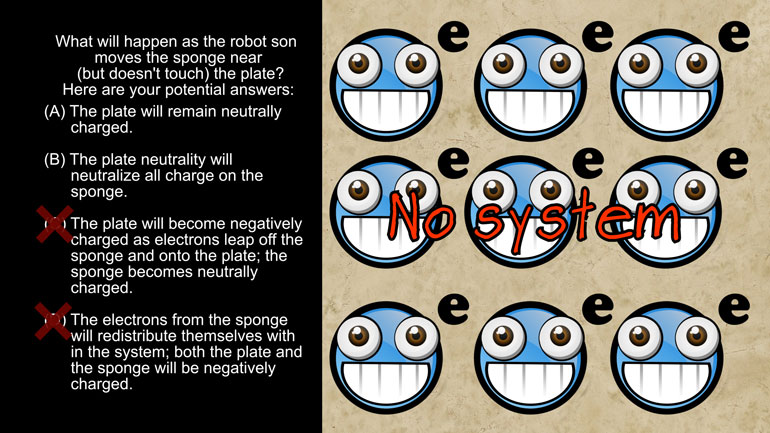
AP Physics 2: 2.2 Properties of Objects and Systems. What will happen as the robot son moves the sponge near (but doesn't touch) the plate?
AP Physics 2: 2.4 Properties of Objects and Systems. How could you show the carnival barker an emission spectrum?