ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Playlist AP® Physics 2: Object Interaction and Forces 7 videos
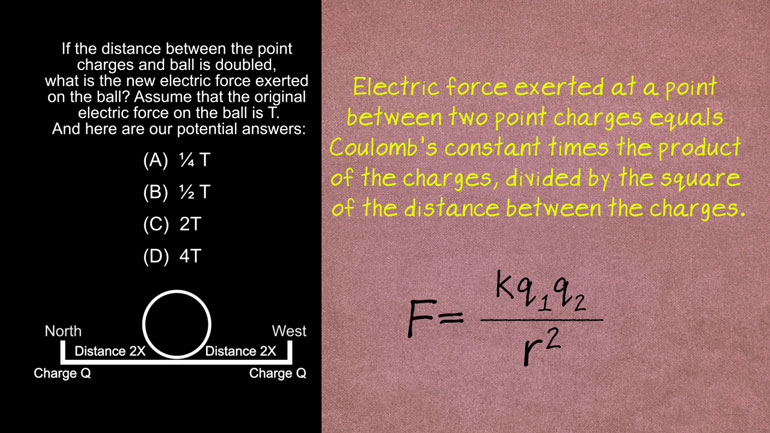
AP Physics 2: 1.2 Object Interaction and Forces. What is the acceleration experienced by the feather?
AP Physics 2: 1.3 Object Interaction and Forces. What is the magnitude of the current L in the wire?
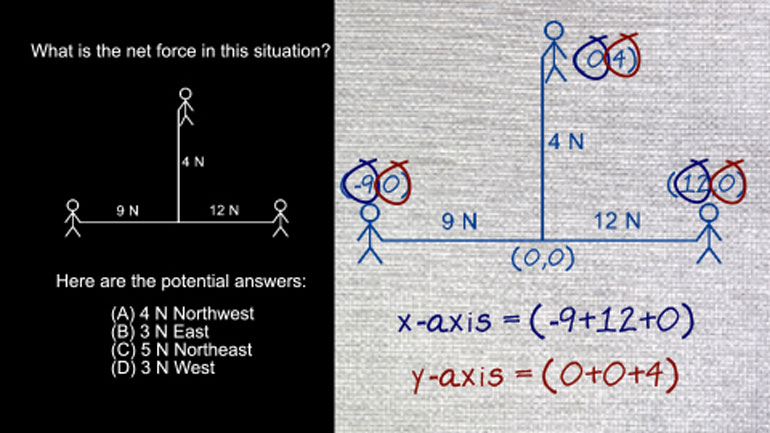
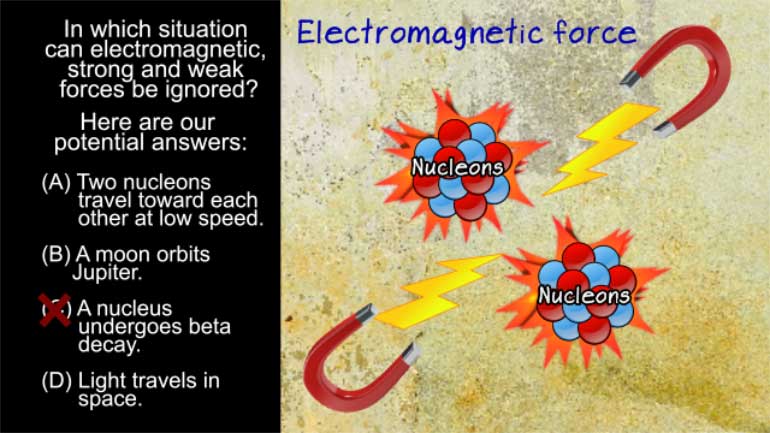
AP Physics 2: 2.1 Object Interaction and Forces. Which of the following is not one of the four fundamental forces?
AP Physics 2: 1.3 Object Interaction and Forces 175 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Physics 2: 1.3 Object Interaction and Forces. What is the magnitude of the current L in the wire?
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak and here's your shmoop du jour
- 00:05
Brought to you by pigeons keeping statue cleaners employed worldwide's
- 00:11
by study count pigeons react to magnetic fields Scientists discovered
- 00:15
the pigeons could sense the earth's magnetic field with their
- 00:18
beaks This allows them to navigate over long distances which
Full Transcript
- 00:22
is perfect for migration seasons you got following figure This
- 00:27
shows a simplified experiment The magnetic field is produced by
- 00:31
a long straight wire And the pigeons beak is treated
- 00:34
as a point charge of plus ten e at a
- 00:37
distance of six centimetres from the wire with the point
- 00:40
charge has a velocity of five meters per second and
- 00:43
is subject to a magnetic force of four times ten
- 00:46
to the negative Twenty second newtons what's the magnitude of
- 00:50
the current l in the wire His s subzero is
- 00:54
approximately twelve times ten to the negative seventh newtons per
- 00:57
ampere square and hear the potential answer Six Twelve eighteen
- 01:00
Twenty four a Wow Pigeons are more impressive than we
- 01:04
thought Well maybe we should stop calling them flying garbage
- 01:07
rats That seems kind of disrespect We need an equation
- 01:11
to find the current in this wire and we need
- 01:13
to figure it out from outside the wire itself Based
- 01:16
off of the magnetic field the current creates around the
- 01:19
wire Let's Scroll through the equations We have crammed into
- 01:23
our brain to see what would work Well The best
- 01:26
equation that used for this is the equation for the
- 01:28
magnitude of a magnetic field which equals that constant of
- 01:32
vacuum permitted ity times the current divided by two pi
- 01:38
times Distance Yeah all right But to use this equation
- 01:41
we first have to find the magnitude of the field
- 01:44
more scrolling Sometimes it feels like if we memorize one
- 01:47
more equation we won't have enough power left over to
- 01:50
remember our own name Okay we can use the equation
- 01:53
for the force of a magnetic field that equals charge
- 01:56
times velocity times the magnitude of the magnetic field right
- 02:00
there and with a little algebraic crust o change Oh
- 02:03
we see that the magnitude of the field equals the
- 02:06
force divided by the charge times the velocity Now we
- 02:10
have two equations that both equal the magnitude of the
- 02:13
magnetic field which means the equations also each other And
- 02:18
we can rearrange the equation to solve for the current
- 02:21
Well finally we can plug in the numbers and do
- 02:23
some math But hold on let's make things easy on
- 02:26
ourselves with a little rounding fir e the unit of
- 02:29
charge will round that up to two times ten to
- 02:32
the negative nineteenth coolum And for pie will round that
- 02:36
down to three Okay we can't stand me into his
- 02:39
patient any longer Let's all this already the current equals
- 02:42
two times pi three times the distance six times ten
- 02:47
to the negative second meters times the force which equals
- 02:51
four times ten to the negative twenty second newton's All
- 02:54
of that is divided by the quantity of charge ten
- 02:57
times two times ten to the negative nineteenth times the
- 03:01
velocity five meters per second time's the electric constant twelve
- 03:06
times ten to the negative seventh newtons per amber's square
- 03:11
But once we put all this together we find that
- 03:13
the current equals twelve amps making answer Be the winner
- 03:16
So we'll give credit where it's due pigeons have super
- 03:18
powered beaks Maybe that would be a cool superhero pigeon
- 03:22
boy able to sense magnetic fields with his known it 00:03:25.738 --> [endTime] is better than another spider man reboot Oh
Related Videos
AP Physics 2: 1.1 Properties of Objects and Systems. What is the magnitude and direction of the conventional current in this wire?
AP Physics 2: 1.5 Properties of Objects and Systems. According to the Bohr's model of the atom, which of the following are true?
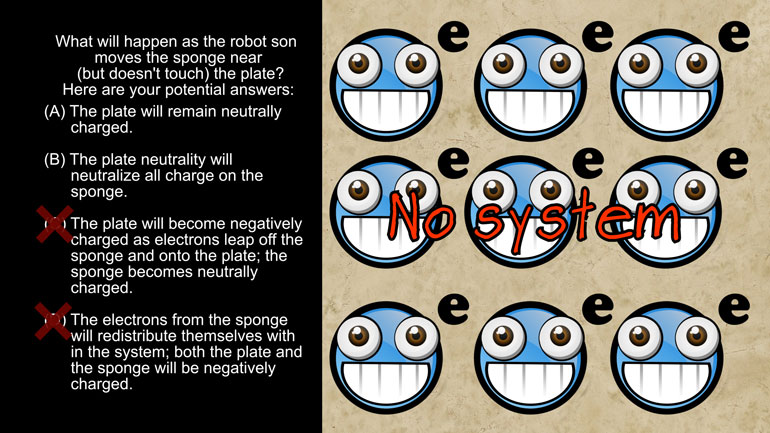
AP Physics 2: 2.2 Properties of Objects and Systems. What will happen as the robot son moves the sponge near (but doesn't touch) the plate?
AP Physics 2: 2.4 Properties of Objects and Systems. How could you show the carnival barker an emission spectrum?