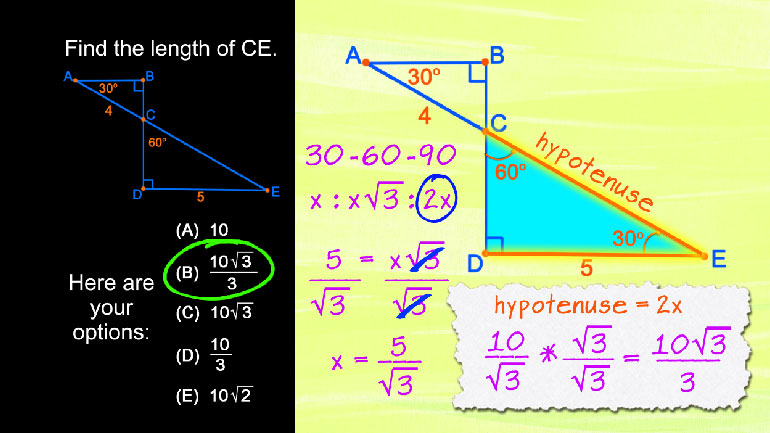
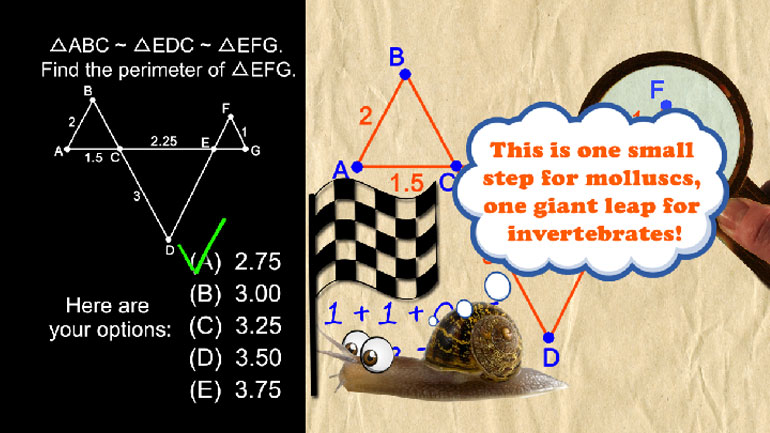
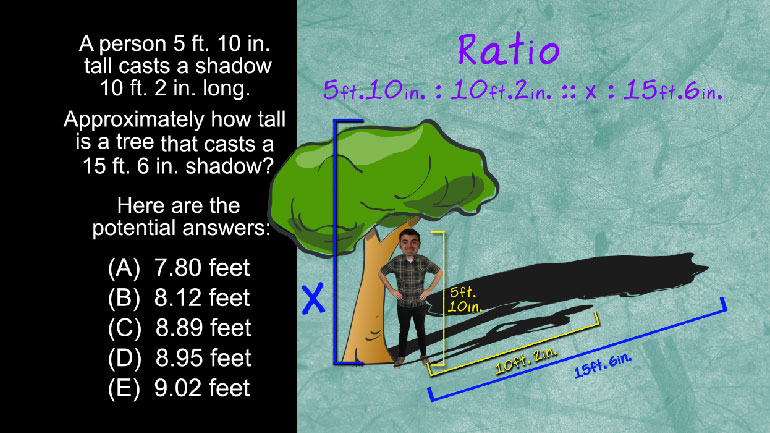
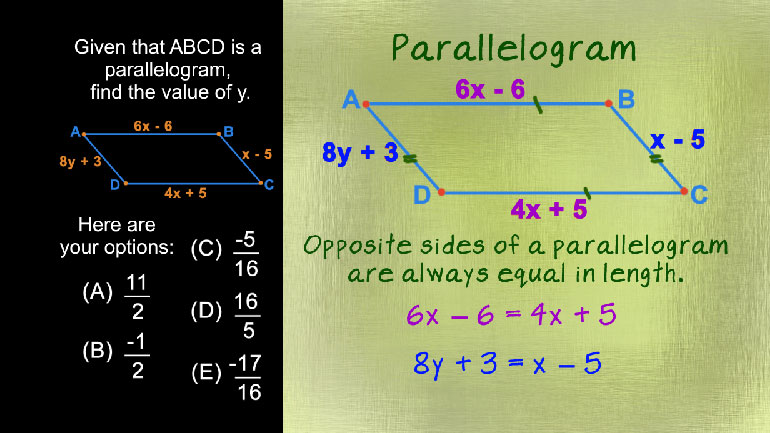
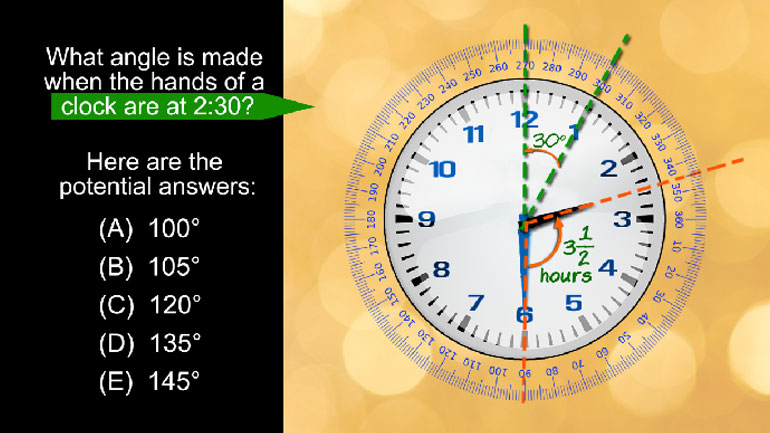
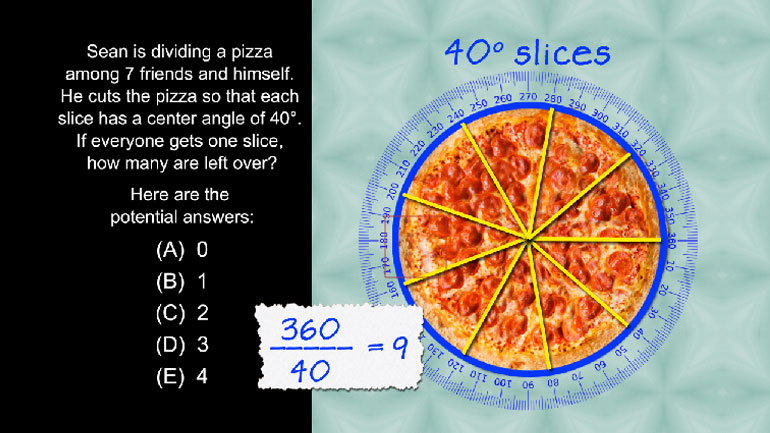
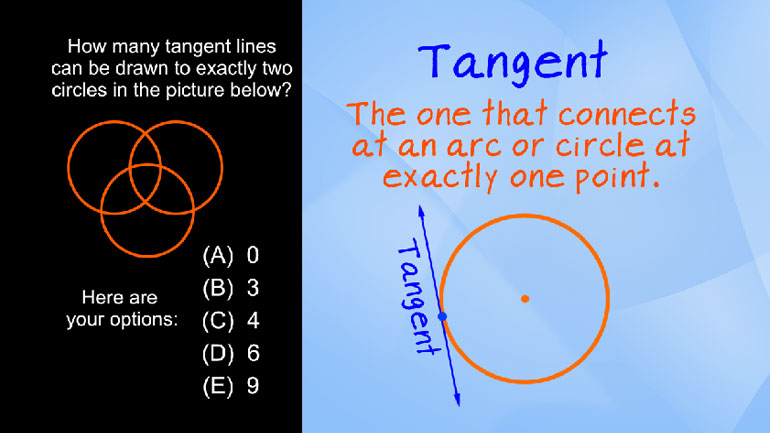
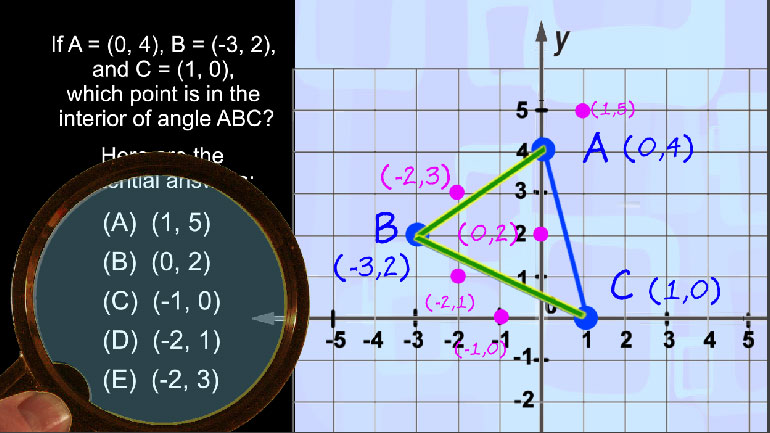
ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
SAT Math 7.4 Geometry and Measurement 205 Views
Share It!
Description:
SAT Math 7.4 Geometry and Measurement
Transcript
- 00:02
Here’s your shmoop du jour, brought to you by a midpoint.
- 00:06
Apparently, it has some kind of restraining order against the circumference.
- 00:17
F is the midpoint of DG and E is the midpoint of FD.
- 00:21
What is the ratio of the area of the circle with center E to the area of the circle with center G?
- 00:29
Here are the potential answers...
Full Transcript
- 00:33
Okay, so we’ve got three circles here…and we want to know how many of the itty-bitty
- 00:37
circles we could fit inside the big circle.
- 00:40
Well, all right…to be more technically accurate, we want a ratio of the area.
- 00:45
And all we can use to get there is a couple of midpoints.
- 00:48
These guys had better be good. Okay… here’s another problem where we’re
- 00:48
going to have to go ahead and just call something “x.”
- 00:48
In this case, we know that ED is a radius of the smallest circle… so we’ll call
- 00:53
that guy “x.”
- 00:54
That would make FD, the smallest circle's diameter, 2x.
- 00:59
And, because FD is also a radius of the medium circle…GD is going to be 4x.
- 01:05
Now that we have our radii, it’s time to whip out the formula for the area of a circle,
- 01:09
and go to work… For our smallest circle, we’ll take the formula
- 01:13
Area equals pi times r squared and plug in our… r…
- 01:20
…to get pi x squared.
- 01:22
For the big circle, we get pi times the quantity 4x… squared… or pi sixteen x squared.
- 01:28
We’re looking for the ratio, which is always the same as a fraction…
- 01:32
…and in this case is pi times x squared over pi times sixteen x squared.
- 01:38
The pi and the x squared cancel out…leaving us with just 1 over 16…
- 01:43
…which is equivalent to option A.
Related Videos
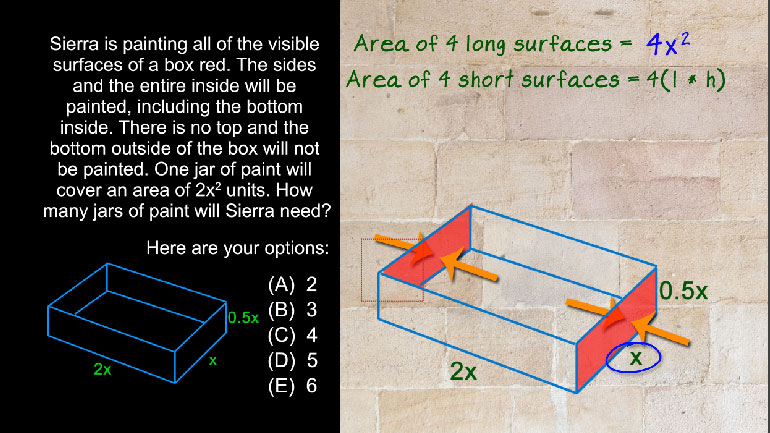
SAT Math 2.1 Geometry and Measurement. What is the measure of angle z in terms of x and y?
In 2014, the unemployment rate of one county in California was 7%. In another county, the unemployment rate was 11%. Which of the following express...
Angela is making cookies for a bake sale. She expects each batch of her cookies to sell for $40. It costs her $10 to make one batch of cookies, and...