ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Computer Science Videos 112 videos
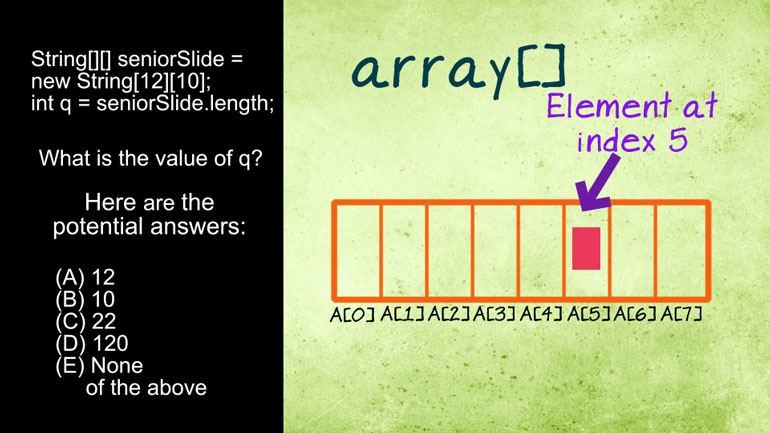
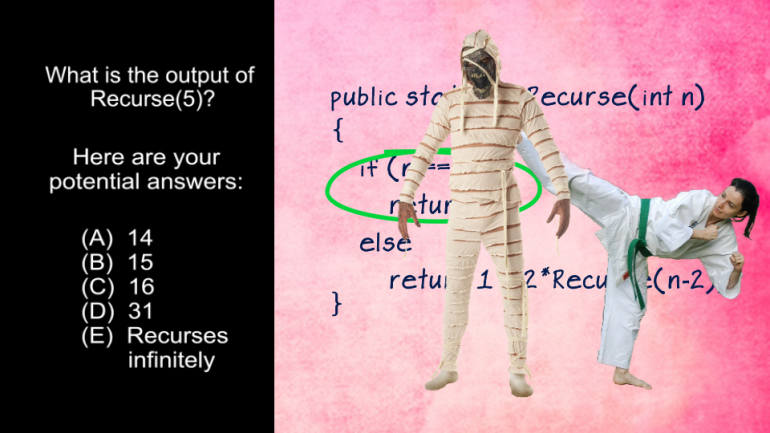
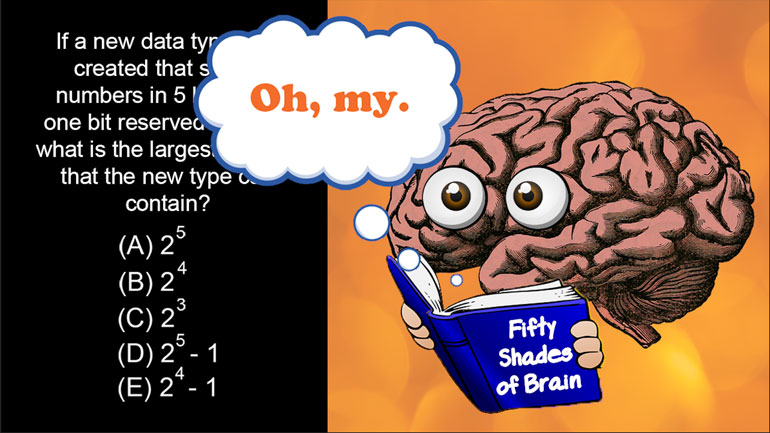
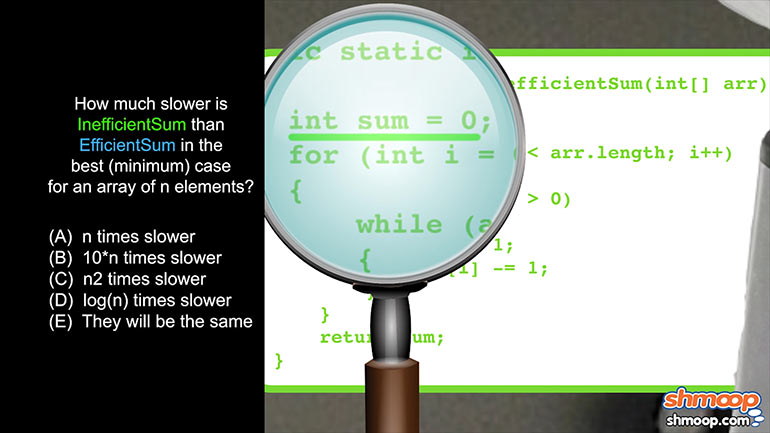
AP Computer Science 1.2 GridWorld Case Study and APIs. What is the direction of the actor?
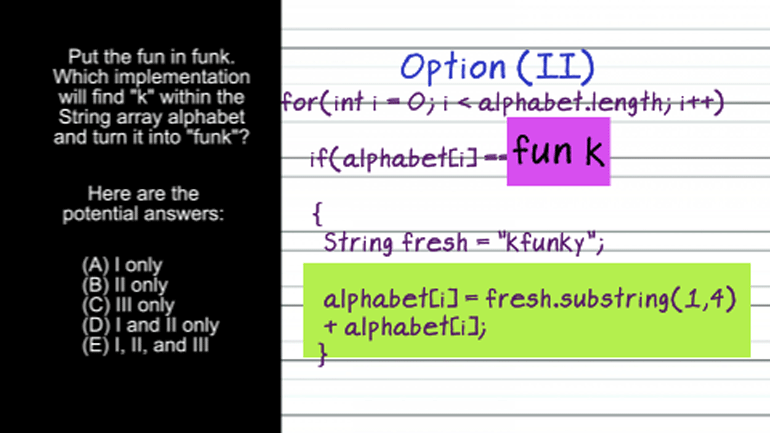
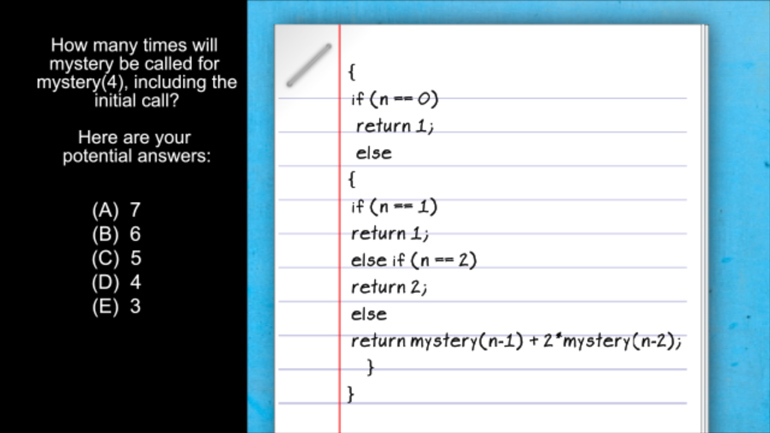
AP Computer Science 1.4 Standard Algorithms. How many times will mystery be called for mystery(n) for n > 1?
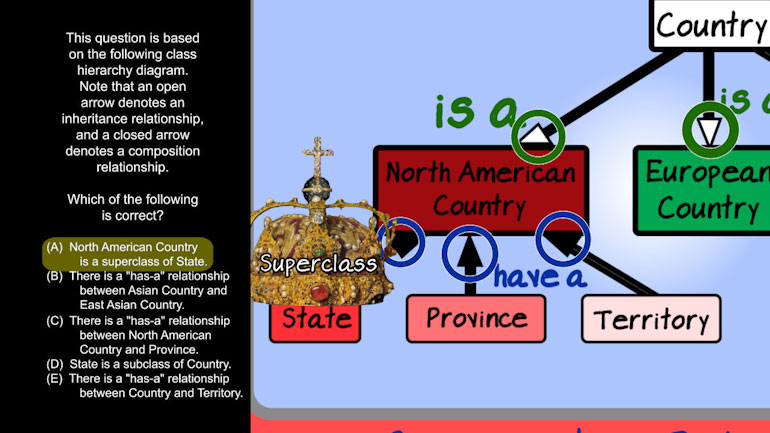
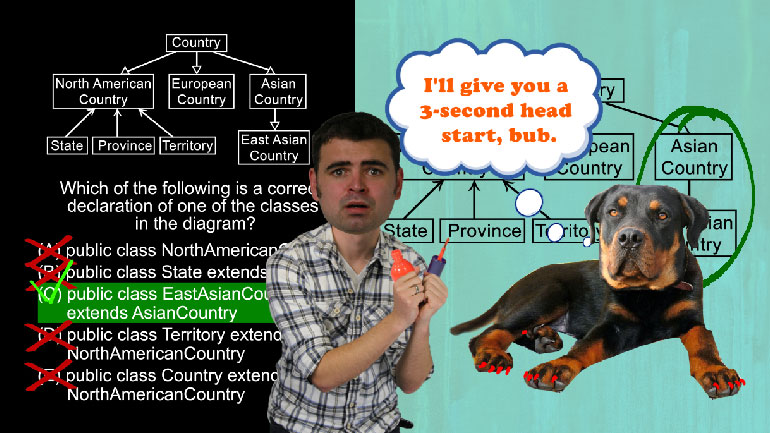
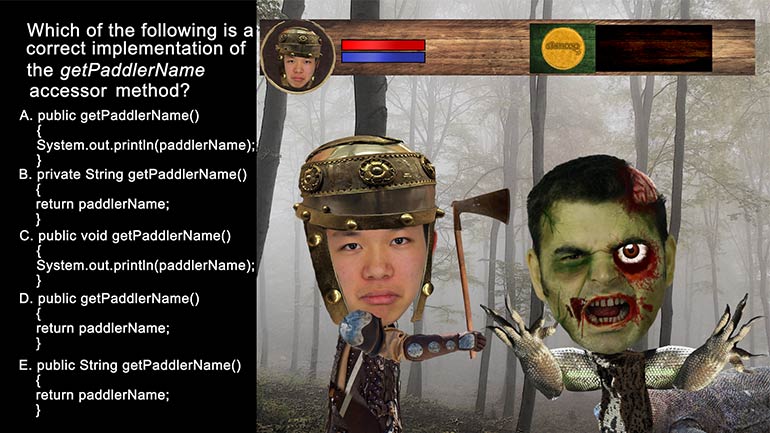
AP Computer Science 2.3 Classes and Objects. Which of the following is correct implementation of the Country class?
AP Computer Science 2.3 Review of the Basics 171 Views
Share It!
Description:
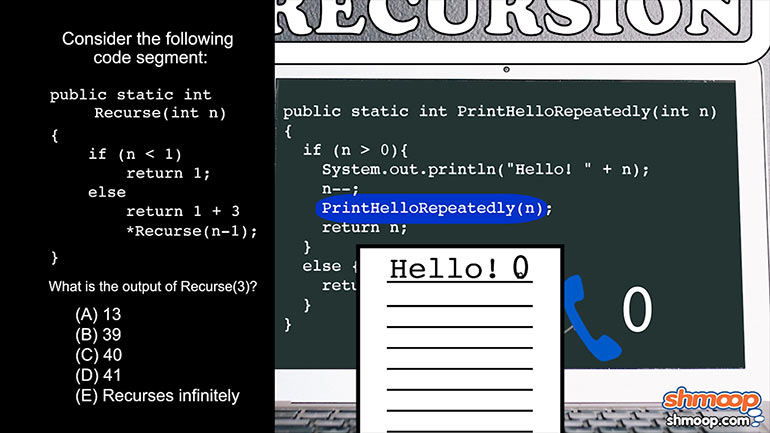
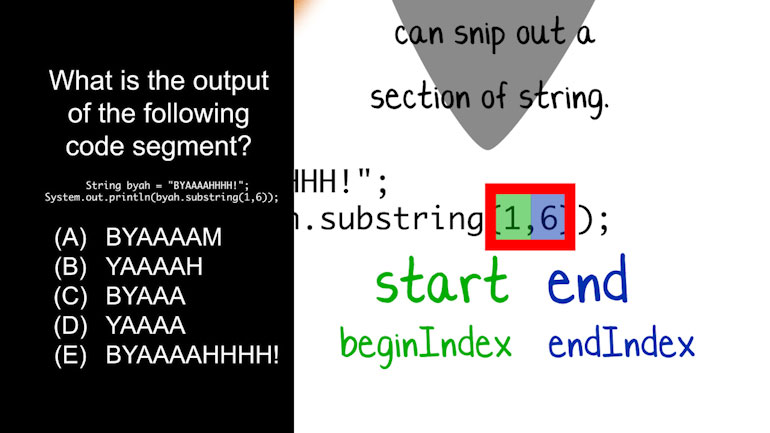
APCS: Review of the Basics Drill 2, Problem 3. What is the output of the following code segment?
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak And here's your shmoop du jour
- 00:05
brought to you by floating point variables there the point
- 00:09
Nine nine nine nine nine and an eight You can
- 00:11
count on what is the output of the following code
- 00:14
segment for a night of eating thai food Keep pressing
Full Transcript
- 00:20
right And here your potential answers Okay true false got
- 00:25
it All right let's Go let's take a look at
- 00:27
what this code segment is trying to do First we
- 00:29
get two double variables The first being given the value
- 00:32
of ten and a second being given the value of
- 00:34
zero Then we start a loop The loop begins counting
- 00:37
with inger i zero halt when i stopped being less
- 00:41
than fifty and increases i buy one each time the
- 00:44
loop like once inside the loop will be adding point
- 00:48
to numb teo over and over and over again fifty
- 00:51
times total since that's how long our loop will run
- 00:55
afterwards we'll have three statements Print results of a few
- 00:58
operations were the first prints the tour false results of
- 01:01
whether numb one equals to the second print through her
- 01:04
false based on whether numb one divided by two equals
- 01:06
one same number and not zero And the third prince
- 01:11
true or false depending on whether numb one minus number
- 01:14
two equal zero again away to check if they're the
- 01:16
same number So let's try and predict the kinds of
- 01:19
results will get All right Back up to our loop
- 01:21
We've got numb to starting out equal to zero and
- 01:25
we add point two two it fifty times Well in
- 01:28
california fifty towns point two is ten so after the
- 01:30
loop is finished running canting treating tonight someone in them
- 01:35
too should both be tense And if we plug that
- 01:39
into our print statements we'd get numb One equals dumb
- 01:41
two or ten equals ten True can divide by ten
- 01:43
equals one true and minus ten equals zero True but
- 01:47
way Just hold your horses one sec If you got
- 01:50
your handy compiler you can pause the video here and
- 01:53
try running the code yourself and no seriously give the
- 01:55
shot will wait here's the code again and a picture
- 01:59
of a cold er Yesterday all my troubles seemed so
- 02:07
far ready All right So what did you find out
- 02:10
Well for those of you who didn't run the code
- 02:12
this is what happened Falls all falls which is our
- 02:16
answered the question by the way option he but wait
- 02:18
Why Tennis Ten right there's Not much That could possibly
- 02:22
go wrong with the statement Tennis Just ten even in
- 02:24
california with all you communists out there But i will
- 02:26
unless tennis somehow not ten Well let's add a line
- 02:30
to the end of the snippet to investigate a little
- 02:32
more closely We'll have it print the actual value of
- 02:35
numb to to make sure we're getting the ten that
- 02:37
we paid for system out print line none too And
- 02:41
go well ten is not ten it's Very very close
- 02:45
But it's just not in this case It's like nine
- 02:49
point nine nine nine nine nine six something that's why
- 02:52
our statements returned false and it's Not even a bug
- 02:55
issue here has to do with the very nature of
- 02:57
floating point arithmetic Those double variables we declared earlier and
- 03:01
more formally known as double precision floating point variables which
- 03:05
is to say is not quite as solid as an
- 03:07
imager it's More like an approximation of a real number
- 03:11
This has its uses when dealing with very complicated numbers
- 03:14
that don't quite need to be perfectly exact The distance
- 03:17
to the next galaxy over for example like that But
- 03:20
when you're dealing with the values that need to be
- 03:22
concrete like money do yourself a favor and compute using
- 03:25
interest or long otherwise you're going to be going people
- 03:29
One craw drill yin of a penny and your knives 00:03:32.22 --> [endTime] probably aren't that shark even against you
Related Videos
AP Computer Science 1.2 GridWorld Case Study and APIs. What is the direction of the actor?
AP Computer Science 1.4 Standard Algorithms. How many times will mystery be called for mystery(n) for n > 1?
AP Computer Science 2.3 Classes and Objects. Which of the following is correct implementation of the Country class?
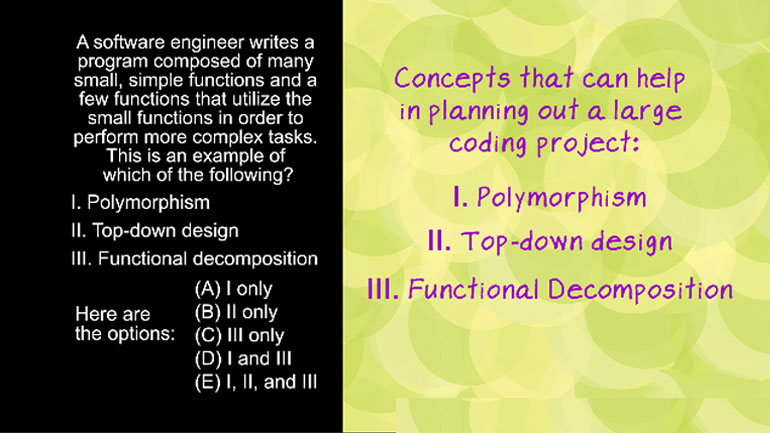
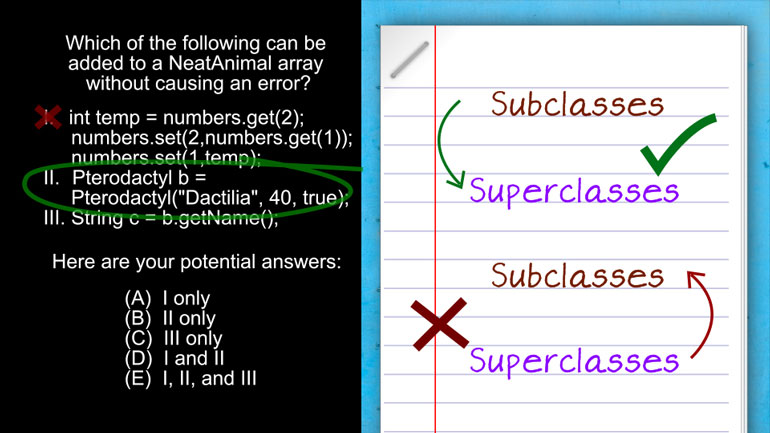
AP Computer Science 3.4 Inheritance, Abstraction, and Polymorphism. Which of the following will satisfy the conditional if statement for boo, str,...
AP Computer Science 4.2 Standard Algorithms. What kind of algorithm is the following?