ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Evolution Videos 10 videos
AP Biology 2.3 Evolution. What did the Urey-Miller experiments do?
AP Biology 4.1 Evolution. When or where is allopatric speciation likely seen?
AP Biology 3.5 Evolution 20 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Biology 3.5 Evolution. What is the reproductive barrier in the video best described as?
Transcript
- 00:04
Here’s your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by
- 00:06
barriers, the sworn enemy of Ronald Reagan. [Raegan smashing down a barrier and Mikhail Gorbachev appears]
- 00:10
Check out the following:
- 00:11
Two neighboring species mate during different seasons.
- 00:15
This reproductive barrier is best described as….what?
Full Transcript
- 00:18
And here are the potential answers: Many species are seasonal breeders based on
- 00:28
favorable conditions, such as abundant food and water supplies.
- 00:31
Many species’ wives wish they were romantic breeders who would bring home flowers and [Rhino wife wishing for more romantic Rhino husband]
- 00:35
chocolates once in a while.
- 00:37
Species like ring-tailed lemurs, horses, hamsters, and groundhogs prefer breeding in spring, [two groundhogs together in a forest]
- 00:42
while sheep, goats, elk, and mice prefer the fall.
- 00:46
Rabbits, however, pay no attention to the calendar. [lots of rabbits together]
- 00:49
Though is this seasonal reproductive barrier best described as “mechanical”?
- 00:53
Well, “mechanical” refers to the fact that some species are unable to mate with [A snake and a turtle side by side]
- 00:58
other species because…well, physically they just can’t.
- 01:02
The mechanics of the process are incompatible, which means A is incorrect.
- 01:07
How about B?
- 01:08
Is seasonal mating a geographical reproductive barrier?
- 01:11
Let’s say a body of water separates one herd of hippos from another. [Two hippo's either side of a body of water]
- 01:16
While that would be a darn shame, it wouldn’t have anything to do with the seasons.
- 01:20
So B isn’t our answer, either. [Hippo entering the ocean]
- 01:22
Let’s look at answer “D”.
- 01:24
A hybrid zygote is formed when no barriers exist to interspecies mating. [A zebra and a horse together and a hybrid of the two appears]
- 01:30
Since this is a pretty big no-no in nature, a post-zygotic reproductive barrier kicks
- 01:36
in to insure that the hybrid is infertile and won’t reproduce. [Hybrid of zebra and horse disappears]
- 01:40
Since “D” is all about isolation mechanisms, we can eliminate it as our correct answer.
- 01:46
That leaves us just with “C,” temporal.
- 01:48
Temporal separation is defined as a mating barrier achieved by differences in the timing
- 01:54
of species’ mating seasons.
- 01:58
Looks like C is our right answer.
- 01:59
Now will someone please get that poor rhino a box of chocolates…? [Two rhinos sniffing for chocolates]
Related Videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
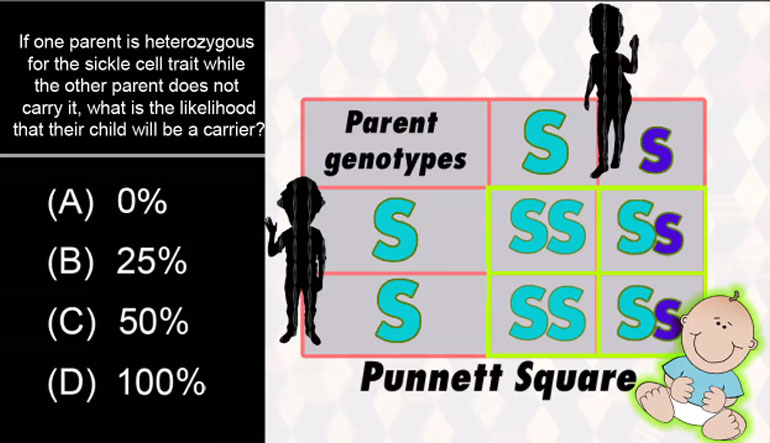
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
AP Biology: Free Energy and Molecular Building Blocks Drill 1, Problem 1. Which statement incorrectly describes the properties of water?
AP® Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 2. What was likely the first genetic material?